The Remaining Useful Life (RUL) of an asset is the estimated length of time remaining before it will need to be replaced.
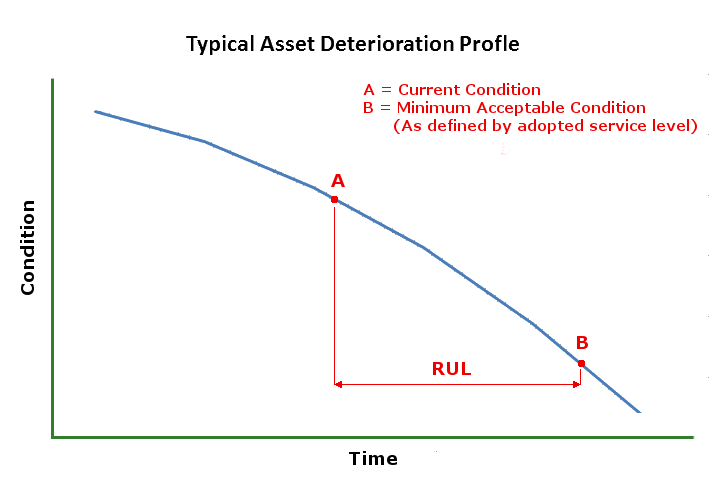
Determining an accurate remaining useful life for an asset is an important step in determining when the asset should be renewed. There are number of factors that will or may effect the RUL of an asset, including;
The Australian Infrastructure Financial Management Guidelines suggest that an asset's age should be used to determine its remaining useful life in the early part of its lifecycle, and that condition should be used near the end of its life after signs of distress have become evident.
The methodology below is based on Muswellbrook Shire Council's trial Effective Remaining Life Evalution Sheet. Condition, Function, and Capacity / Utilisation are considered, and the attribute assigned the worst score is used to determine the asset's RUL.
| Score | Condition | Wear | Maintenance Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Chance of failure is minimal | Negligible wear | No problem beyond normal maintenance |
| 2 | Chance of failure is minimal | All wear within design tolerance | No problem beyond normal maintenance |
| 3 | Chance of failure is low but present | Wear approaching allowable limits | Problem that will require future attention |
| 4 | There is a real chance of failure | Wear beyond allowable limits | Problem identified requiring immediate attention |
| 5 | Failed | Substantial deterioration | Dangerous or Broken down |
| Score | Functionality | Obsolescence | Regulatory |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Easily performing required function | Up-to-date | Meets regulatory requirement |
| 2 | Adequately performing required function | Acceptable | Meets regulatory requirement |
| 3 | Performing function but possibly not effectively | Dated but meeting need. | Minor regulatory infraction. Modification may meet short-term need |
| 4 | At lowest level of acceptability in performing required function | Out-of-date, just tolerable | Regulatory requirement necessitates planned renewal |
| 5 | Not performing function | Redundant | Does not meet regulatory requirement |
| Score | Capacity | Utilisation | Climatic Influence/Economic benefit to repair |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Easily meeting existing and future load | Repeatedly utilised | No damage |
| 2 | Adequately meeting existing and future load | Frequently utilised | Aesthetic damage only eg watermarked, minor vandalism |
| 3 | Usually meets existing load; occasional failure with financial consequence | Moderate utilisation; reduced economic benefit. | Moderate damage. Repair is cost effective but does not return full functionality |
| 4 | Frequently fails to meet existing load. Unlikely to meet future load. | Infrequent utilisation; poor economic benefit | Damage necessitates planned renewal. Not cost effective to repair |
| 5 | Unable to meet existing or future load | Not utilised | Damaged to point of failure |
The relationship between the score assigned and RUL may vary depending on the deterioration profile of the asset type being considered, but the table below gives some indicative figures.
| Worst Score | Life Remaining |
| 1 | 95% |
| 2 | 75% |
| 3 | 40% |
| 4 | 15% |
| 5 | 1 year |